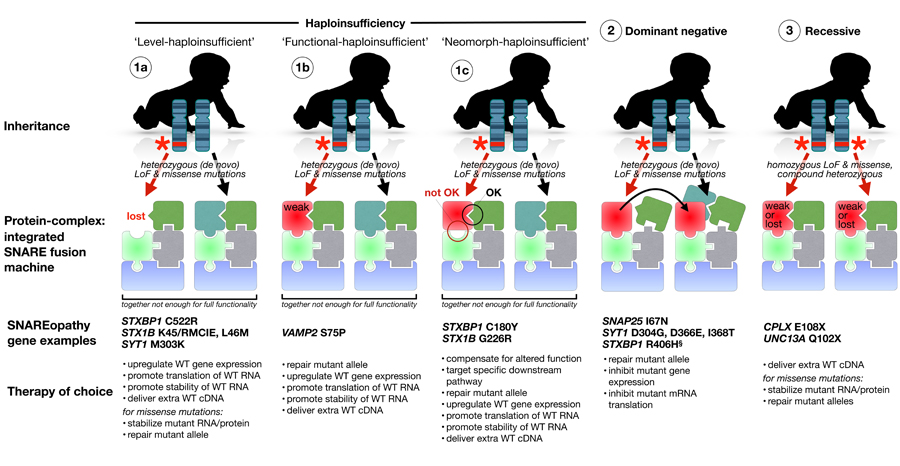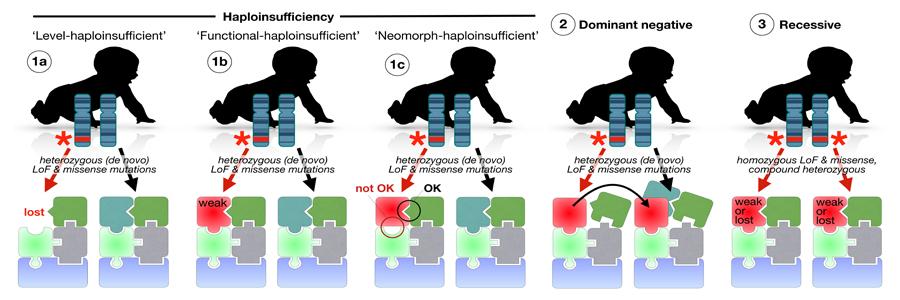
A position paper by Verhage & Sorensen published in Neuron on June 19 proposes to unify syndromes caused by mutations in eight core components of the synaptic secretion machinery, based on common etiology and mechanism
The neuronal SNAREs and their key regulators together drive synaptic vesicle exocytosis and synaptic transmission as a single, integrated membrane fusion-machine. Human pathogenic mutations are now reported for all eight core components, but patients are diagnosed with very different neurodevelopmental syndromes: children carrying mutations in a single SNAREopathy gene can have >20 different diagnoses, depending on how they entered the health care system (see summary here), a situation referred to as the diagnostic odyssey for the families/caretakers. A new functional classification, as SNAREopathies, provides key advantages to (1) delineate a clinical subgroup with a common pathogenic starting point, (2) end the diagnostic odyssey for patient families, (3) contribute to the elucidation of pathogenic pathways towards clinical neurodevelopmental phenotypes and (4) eventually to develop intervention strategies.

The paper is available here